Data-Driven Batch Localization and SLAM Using Koopman Linearization
Z. Guo
F. Dümbgen
J. Forbes
T. D. Barfoot
IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024
IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024
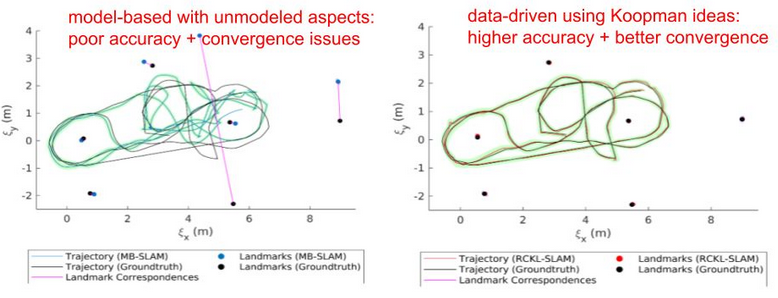
One-sentence summary
Instead of solving state estimation in the original space where measurement and motion functions are non-linear; lift the problem to a higher-dimensional state where they become linear, such that system identification becomes a linear least-squares problem and state estimation empirically converges to better solutions.
Abstract
We present a framework for model-free batch localization and SLAM. We use lifting functions to map a control-affine system into a high-dimensional space, where both the process model and the measurement model are rendered bilinear. During training, we solve a least-squares problem using groundtruth data to compute the high-dimensional model matrices associated with the lifted system purely from data. At inference time, we solve for the unknown robot trajectory and landmarks through an optimization problem, where constraints are introduced to keep the solution on the manifold of the lifting functions. The problem is efficiently solved using a sequential quadratic program (SQP), where the complexity of an SQP iteration scales linearly with the number of timesteps. Our algorithms, called Reduced Constrained Koopman Linearization Localization (RCKL-Loc) and Reduced Constrained Koopman Linearization SLAM (RCKL-SLAM), are validated experimentally in simulation and on two datasets: one with an indoor mobile robot equipped with a laser rangefinder that measures range to cylindrical landmarks, and one on a golf cart equipped with RFID range sensors. We compare RCKL-Loc and RCKL-SLAM with classic model-based nonlinear batch estimation. While RCKL-Loc and RCKL-SLAM have similar performance compared to their model-based counterparts, they outperform the model-based approaches when the prior model is imperfect, showing the potential benefit of the proposed data-driven technique.
[Paper] [arXiv]